- Understanding Multi-Touch Attribution Model Decision-Making
- What is the multi-touch attribution approach?
- What's the difference between mmm and mta?
- What is the preferred method of multi-touch attribution to get the most valid results?
- What do multiple touchpoints mean?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
In today’s digital marketing landscape, understanding the customer journey is more complex than ever. With multiple touchpoints across various channels, businesses face the challenge of accurately attributing value to each interaction. Multi-touch attribution models have emerged as a critical tool for marketers seeking to optimize their strategies and allocate resources effectively. These models provide a nuanced view of how different marketing efforts contribute to conversions, enabling data-driven decision-making. By analyzing the impact of each touchpoint, businesses can gain deeper insights into customer behavior, improve campaign performance, and maximize return on investment. This article explores the decision-making process behind selecting and implementing the right multi-touch attribution model for your business.
Understanding Multi-Touch Attribution Model Decision-Making
What is Multi-Touch Attribution?
Multi-Touch Attribution (MTA) is a method used in marketing to determine the value of each customer touchpoint leading to a conversion. Unlike single-touch models, which credit only one interaction, MTA distributes credit across multiple touchpoints, providing a more comprehensive view of the customer journey. This approach helps marketers understand which channels and campaigns are most effective in driving conversions.
See Also Multi-Touch Attribution Model Decision-Making
Multi-Touch Attribution Model Decision-MakingTypes of Multi-Touch Attribution Models
There are several types of MTA models, each with its own way of assigning credit to touchpoints:
- Linear Attribution: Distributes credit equally across all touchpoints.
- Time Decay Attribution: Gives more credit to touchpoints closer to the conversion.
- Position-Based Attribution: Allocates 40% of the credit to the first and last touchpoints, and the remaining 20% is distributed among the middle touchpoints.
- Data-Driven Attribution: Uses algorithms and machine learning to assign credit based on historical data.
Benefits of Using Multi-Touch Attribution
Using MTA offers several advantages:
- Improved Marketing ROI: By understanding which touchpoints contribute most to conversions, marketers can allocate budgets more effectively.
- Enhanced Customer Insights: MTA provides a deeper understanding of customer behavior and preferences.
- Better Campaign Optimization: Marketers can refine campaigns based on data-driven insights, leading to more effective strategies.
 Multi-Touch Attribution Model Decision-Making
Multi-Touch Attribution Model Decision-MakingChallenges in Implementing Multi-Touch Attribution
Despite its benefits, implementing MTA can be challenging:
- Data Complexity: MTA requires collecting and analyzing large amounts of data from multiple sources.
- Integration Issues: Ensuring all marketing channels and tools are integrated can be difficult.
- Attribution Accuracy: Determining the exact contribution of each touchpoint can be complex, especially in long and non-linear customer journeys.
Best Practices for Multi-Touch Attribution Decision-Making
To effectively use MTA, consider the following best practices:
- Define Clear Objectives: Understand what you want to achieve with MTA, whether it's improving ROI, optimizing campaigns, or gaining customer insights.
- Choose the Right Model: Select an MTA model that aligns with your business goals and customer journey complexity.
- Ensure Data Quality: Accurate and comprehensive data is crucial for reliable attribution.
- Regularly Review and Adjust: Continuously monitor and adjust your attribution model to reflect changes in customer behavior and market conditions.
 Multi-Touch Attribution Model Decision-Making
Multi-Touch Attribution Model Decision-Making| Model | Description | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Attribution | Distributes credit equally across all touchpoints. | When all touchpoints are considered equally important. |
| Time Decay Attribution | Gives more credit to touchpoints closer to the conversion. | When the final interactions are most influential. |
| Position-Based Attribution | Allocates 40% of the credit to the first and last touchpoints, and the remaining 20% is distributed among the middle touchpoints. | When the first and last interactions are critical. |
| Data-Driven Attribution | Uses algorithms and machine learning to assign credit based on historical data. | When you have sufficient data and want a highly accurate model. |
What is the multi-touch attribution approach?
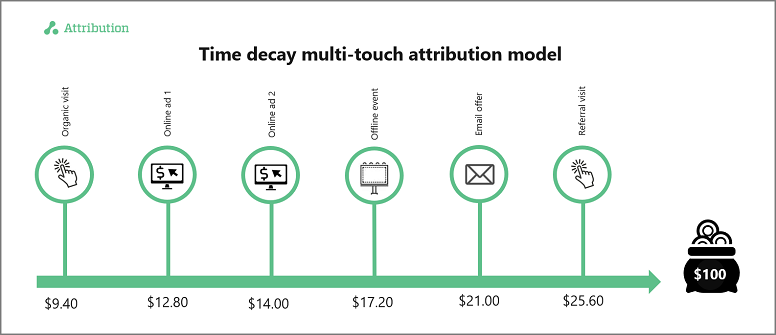
What is Multi-Touch Attribution?
Multi-touch attribution is a marketing analytics approach that assigns credit to multiple touchpoints in a customer's journey before a conversion occurs. Unlike single-touch models, which credit only one interaction, multi-touch attribution recognizes the complexity of modern customer journeys by distributing value across various channels and touchpoints. This method helps marketers understand which interactions contribute most effectively to conversions, enabling better optimization of marketing strategies.
Why is Multi-Touch Attribution Important?
Multi-touch attribution is crucial because it provides a more accurate and comprehensive view of how marketing efforts influence customer decisions. By analyzing multiple touchpoints, businesses can:
- Identify high-performing channels and allocate budgets more effectively.
- Understand customer behavior across different stages of the buying journey.
- Optimize marketing strategies by focusing on the most impactful interactions.
Types of Multi-Touch Attribution Models
There are several types of multi-touch attribution models, each with its own method of assigning credit to touchpoints. The most common models include:
- Linear Attribution: Distributes credit equally across all touchpoints.
- Time Decay Attribution: Gives more credit to touchpoints closer to the conversion.
- Position-Based Attribution: Assigns 40% of the credit to the first and last touchpoints, with the remaining 20% distributed among intermediate interactions.
Benefits of Using Multi-Touch Attribution
Implementing multi-touch attribution offers numerous advantages for businesses, such as:
- Improved ROI measurement by accurately tracking the impact of each marketing channel.
- Enhanced decision-making through data-driven insights into customer journeys.
- Better resource allocation by identifying underperforming channels and reallocating budgets.
Challenges of Multi-Touch Attribution
While multi-touch attribution is highly beneficial, it also comes with certain challenges, including:
- Data complexity: Managing and analyzing large volumes of data from multiple sources can be overwhelming.
- Integration issues: Combining data from different platforms and tools may require advanced technical expertise.
- Model selection: Choosing the right attribution model for specific business goals can be difficult.
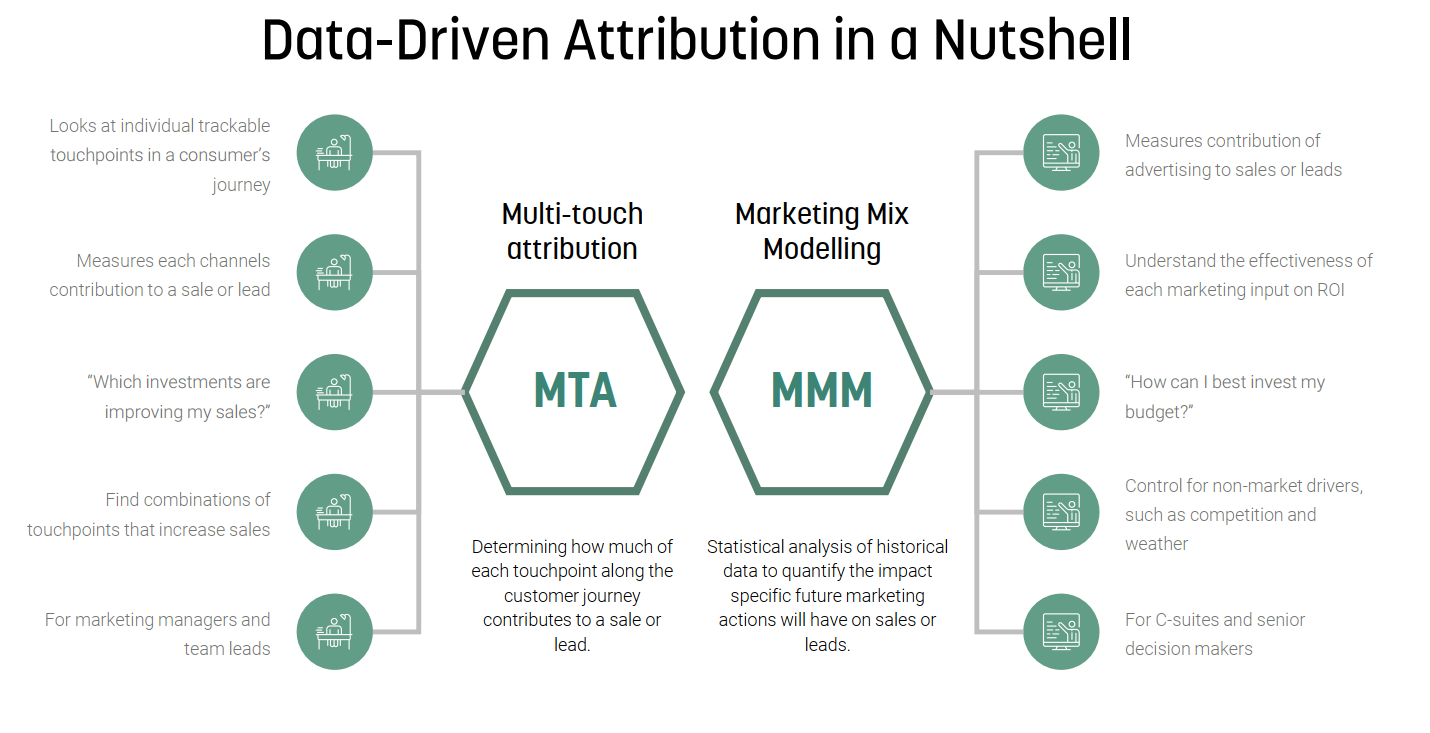
What's the difference between mmm and mta?
What is MMM?
MMM stands for Mavrodi Mondial Moneybox, a decentralized financial system created by Sergey Mavrodi. It operates as a peer-to-peer lending platform where participants help each other by providing financial support without the involvement of traditional banking systems. Key features include:
- No central authority: It is entirely community-driven.
- Voluntary participation: Users join and contribute willingly.
- High-risk model: Returns are not guaranteed and depend on new participants joining.
What is MTA?
MTA refers to Metropolitan Transportation Authority, a public benefit corporation responsible for transportation in the New York metropolitan area. It manages subways, buses, and commuter rail systems. Key aspects include:
- Public service: Provides essential transportation services to millions.
- Government-regulated: Operates under state and federal guidelines.
- Revenue sources: Funded through fares, taxes, and government subsidies.
Purpose and Functionality
The purpose of MMM is to create a decentralized financial network where users can request and provide financial assistance. In contrast, MTA focuses on transportation infrastructure and ensuring efficient mobility for the public. Key differences include:
- MMM: Financial support through community contributions.
- MTA: Physical transportation services for daily commuters.
- MMM: High-risk, non-guaranteed returns.
- MTA: Reliable, regulated public service.
Operational Structure
The operational structure of MMM is based on a peer-to-peer model, where users directly interact without intermediaries. MTA, on the other hand, operates as a centralized organization with a hierarchical management system. Key distinctions include:
- MMM: Decentralized and community-driven.
- MTA: Centralized with a clear chain of command.
- MMM: No physical infrastructure.
- MTA: Extensive physical infrastructure like trains and buses.
Risk and Reliability
MMM is considered high-risk due to its reliance on new participants to sustain payouts, making it volatile and unpredictable. MTA, however, is a reliable public service with consistent operations and government backing. Key points include:
- MMM: High potential for financial loss.
- MTA: Stable and dependable transportation services.
- MMM: No regulatory oversight.
- MTA: Subject to strict government regulations.
What is the preferred method of multi-touch attribution to get the most valid results?
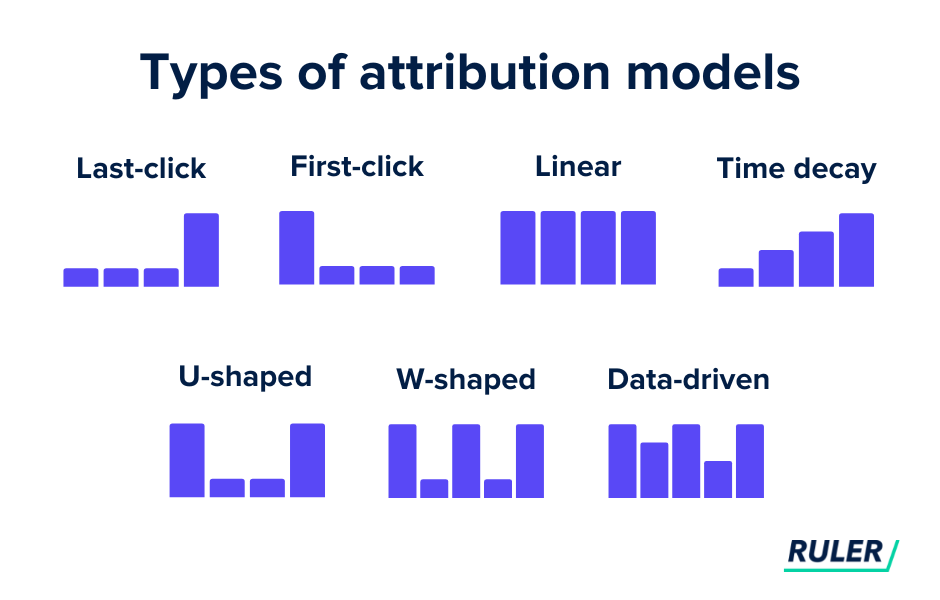
Understanding Multi-Touch Attribution Models
Multi-touch attribution models are designed to distribute credit for a conversion across multiple touchpoints in a customer's journey. The preferred method depends on the business goals and the complexity of the customer journey. Here are the most common models:
- Linear Attribution: Distributes credit equally across all touchpoints.
- Time Decay Attribution: Gives more credit to touchpoints closer to the conversion.
- Position-Based Attribution: Allocates 40% of the credit to the first and last touchpoints, and 20% to the middle ones.
- Data-Driven Attribution: Uses machine learning to assign credit based on historical data and patterns.
Why Data-Driven Attribution is Preferred
Data-driven attribution is often considered the most valid method because it relies on actual customer behavior and historical data. Here’s why it stands out:
- Accuracy: It uses real data to assign credit, reducing biases.
- Flexibility: Adapts to unique customer journeys and marketing strategies.
- Insights: Provides actionable insights by identifying high-performing touchpoints.
Challenges in Implementing Multi-Touch Attribution
While multi-touch attribution offers valuable insights, implementing it comes with challenges:
- Data Integration: Requires combining data from multiple sources, which can be complex.
- Resource Intensive: Needs advanced tools and expertise to analyze data effectively.
- Privacy Concerns: Must comply with data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Steps to Choose the Right Attribution Model
Selecting the right model depends on your business needs. Follow these steps:
- Define Goals: Identify what you want to achieve with attribution (e.g., optimizing ad spend).
- Analyze Customer Journeys: Understand how customers interact with your brand.
- Test Models: Experiment with different models to see which aligns best with your goals.
Tools for Effective Multi-Touch Attribution
Using the right tools is crucial for accurate multi-touch attribution. Here are some popular options:
- Google Analytics: Offers basic attribution models and is widely accessible.
- Adobe Analytics: Provides advanced data-driven attribution capabilities.
- Attribution Software: Specialized tools like AppsFlyer or Adjust for in-depth analysis.
What do multiple touchpoints mean?

What Are Multiple Touchpoints?
Multiple touchpoints refer to the various points of interaction between a customer and a brand throughout the customer journey. These interactions can occur across different channels, platforms, or stages, and they play a crucial role in shaping the customer experience. For example, a customer might first hear about a product through a social media ad, visit the website, and then make a purchase in a physical store. Each of these interactions is a touchpoint.
- Channels: Touchpoints can occur on digital platforms like websites, social media, or email, as well as offline channels like in-store visits or phone calls.
- Stages: They can happen at different stages of the customer journey, such as awareness, consideration, purchase, or post-purchase support.
- Impact: Each touchpoint influences the customer's perception of the brand and their decision-making process.
Why Are Multiple Touchpoints Important?
Multiple touchpoints are essential because they allow brands to engage with customers in a more holistic and consistent manner. By ensuring that each interaction is seamless and aligned with the brand's values, companies can build stronger relationships with their audience. This approach also helps in creating a unified customer experience, which can lead to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
- Consistency: Ensures that the brand message remains uniform across all platforms.
- Engagement: Provides multiple opportunities to connect with customers and address their needs.
- Loyalty: Enhances customer retention by delivering a positive and memorable experience at every stage.
Types of Multiple Touchpoints
There are several types of touchpoints that brands can utilize to interact with their customers. These can be categorized into digital, physical, and human touchpoints. Each type serves a unique purpose and contributes to the overall customer experience.
- Digital Touchpoints: Include websites, mobile apps, social media platforms, and email campaigns.
- Physical Touchpoints: Encompass in-store experiences, product packaging, and printed materials like brochures.
- Human Touchpoints: Involve direct interactions with customer service representatives, sales teams, or support staff.
How to Optimize Multiple Touchpoints
Optimizing multiple touchpoints involves ensuring that each interaction is efficient, relevant, and valuable to the customer. This requires a deep understanding of the customer journey and the ability to tailor experiences based on individual preferences and behaviors.
- Data Analysis: Use customer data to identify patterns and preferences, enabling personalized interactions.
- Integration: Ensure that all touchpoints are interconnected and provide a seamless experience across channels.
- Feedback: Collect and act on customer feedback to continuously improve the quality of interactions.
Challenges of Managing Multiple Touchpoints
While multiple touchpoints offer numerous benefits, they also present challenges that brands must address. These include maintaining consistency, managing complexity, and ensuring data privacy across all interactions.
- Consistency: Ensuring that the brand message and experience are uniform across all touchpoints can be difficult, especially with a large number of channels.
- Complexity: Managing and coordinating multiple touchpoints requires significant resources and coordination.
- Data Privacy: Protecting customer data across various platforms is critical to maintaining trust and compliance with regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is a Multi-Touch Attribution Model and how does it impact decision-making?
A Multi-Touch Attribution Model is a method used in marketing to assign credit to various touchpoints a customer interacts with before converting. Unlike single-touch models, which credit only one interaction, multi-touch models provide a more comprehensive view of the customer journey. This approach helps businesses understand the effectiveness of each marketing channel and campaign, enabling better decision-making by allocating resources to the most impactful strategies. By analyzing the entire customer journey, companies can optimize their marketing efforts and improve ROI.
What are the different types of Multi-Touch Attribution Models?
There are several types of Multi-Touch Attribution Models, each with its own way of distributing credit across touchpoints. Common models include Linear Attribution, which assigns equal credit to all interactions; Time Decay Attribution, which gives more credit to touchpoints closer to the conversion; Position-Based Attribution, which allocates 40% of the credit to the first and last interactions and 20% to the middle ones; and Data-Driven Attribution, which uses algorithms to assign credit based on historical data. Choosing the right model depends on the business's goals and the complexity of the customer journey.
Why is Multi-Touch Attribution important for marketing strategy?
Multi-Touch Attribution is crucial for developing an effective marketing strategy because it provides a detailed understanding of how different channels and campaigns contribute to conversions. By identifying which touchpoints are most influential, businesses can make data-driven decisions to optimize their marketing mix. This approach helps avoid overspending on underperforming channels and ensures that resources are directed toward the most effective strategies. Additionally, it fosters better collaboration between teams by providing a clear picture of each channel's role in driving results.
What challenges are associated with implementing Multi-Touch Attribution Models?
Implementing Multi-Touch Attribution Models can be challenging due to the complexity of tracking and analyzing multiple touchpoints across various channels. One major challenge is data integration, as businesses often use multiple platforms that may not seamlessly share data. Another issue is the accuracy of the data, as incomplete or incorrect tracking can lead to misleading insights. Additionally, selecting the right model requires a deep understanding of the customer journey and the ability to adapt as behaviors change. Despite these challenges, the insights gained from multi-touch attribution can significantly enhance marketing effectiveness when implemented correctly.
Leave a Reply


Articles of interest